ESPRIT
ESPRIT (Estimation of Signal Parameters via Rotational Invariant Techniques) — численный метод, позволяющий оценить параметры суммы синусоид на фоне шумов по серии измерений.
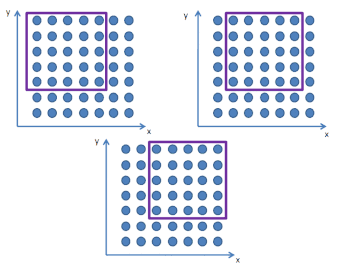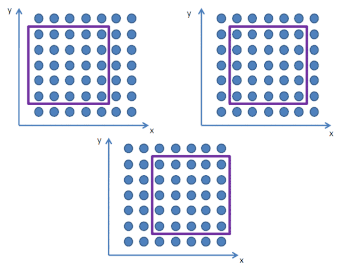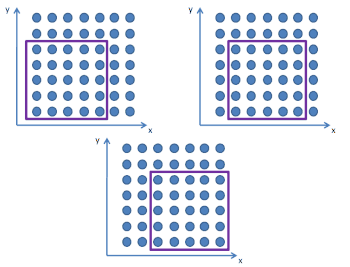
Пример формирования подмасивов в методе 2D ESPRIT
Пример алгоритма
Алгоритм реализации метода ESPRIT в MATLAB:
function esprit(y, model_order, number_of_sources):
m = model_order
n = number_of_sources
create covariance matrix R, from the noisy measurements y. Size of R will be (m-by-m).
compute the svd of R
[U, E, V] = svd(R)
obtain the orthonormal eigenvectors corresponding to the sources
S = U(:, 1:n)
split the orthonormal eigenvectors in two
S1 = S(1:m-1, :) and S2 = S(2:m, :)
compute P via LS (MATLAB's backslash operator)
P = S1\S2
find the angles of the eigenvalues of P
w = angle(eig(P))
return w
Применение
- Оценивание частот и угловых координат источников сигналов в цифровых антенных решётках[3][4].
См. также
Примечания
- Paulraj, A.; Roy, R. & Kailath, T. (1985), Estimation Of Signal Parameters Via Rotational Invariance Techniques - Esprit, Nineteenth Asilomar Conference on Circuits, Systems and Computers, с. 83–89, ISBN 978-0-8186-0729-5, DOI 10.1109/ACSSC.1985.671426
- Roy, R., & Kailath, T. (1989). Esprit-estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariance techniques. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 37(7), 984—995. https://doi.org/10.1109/29. 32276
- Volodymyr Vasylyshyn. Direction of arrival estimation using ESPRIT with sparse arrays.// Proc. 2009 European Radar Conference (EuRAD). — 30 Sept.-2 Oct. 2009. — Pp. 246—249. —
- Василишин В. И. Спектральный анализ методом ESPRIT при предварительной обработке данных методом SSA.// Системи обробки інформації.- 2015. -№ 15. — С. 12 −15.
Литература
- Paulraj, A.; Roy, R. & Kailath, T. (1985), Estimation Of Signal Parameters Via Rotational Invariance Techniques - Esprit, Nineteenth Asilomar Conference on Circuits, Systems and Computers, с. 83–89, ISBN 978-0-8186-0729-5, DOI 10.1109/ACSSC.1985.671426.
- Roy, R.; Kailath, T. (1989). “Esprit - Estimation Of Signal Parameters Via Rotational Invariance Techniques” (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. 37 (7): 984—995. DOI:10.1109/29.32276. Архивировано из оригинала (PDF) 2020-09-26. Дата обращения 2020-07-23. Используется устаревший параметр
|deadlink=(справка). - Ibrahim, A. M.; Marei, M. I.; Mekhamer, S. F.; Mansour, M. M. (2011). “An Artificial Neural Network Based Protection Approach Using Total Least Square Estimation of Signal Parameters via the Rotational Invariance Technique for Flexible AC Transmission System Compensated Transmission Lines”. Electric Power Components and Systems. 39 (1): 64—79. DOI:10.1080/15325008.2010.513363.
- Haardt, M., Zoltowski, M. D., Mathews, C. P., & Nossek, J. (1995, May). 2D unitary ESPRIT for efficient 2D parameter estimation. In icassp (pp. 2096—2099). IEEE.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.