Гладиус (головоногие)
Гладиус — декальцинированная хитиновая пластинка или «стрелка», поддерживающая тело некоторых головоногих. Является рудиментом внутренней раковины[1]. Гладиус есть у головоногих надотряда Десятирукие (кальмаров) и одного современного члена надотряда Восьмируких — Адского кальмара-вампира (Vampyroteuthis infernalis)[1]. Гладиус расположен вдоль спинной части мантии и обычно тянется по всей длине тела. Он находится внутри особой железы — раковинного мешка, клетки которого секретируют основные компоненты гладиуса[1][2].


Гладиусы известны у ряда вымерших головоногих, таких как Teudopseina ( Actinosepia, Glyphiteuthis, Muensterella, Palaeololigo, Teudopsinia, Teudopsis и Trachyteuthis), Loligosepiina (e.g. Geopeltis, Jeletzkyteuthis и Loligosepia) и Prototeuthina (Dorateuthis, Paraplesioteuthis и Plesioteuthis)[3][4].
Разнообразие форм
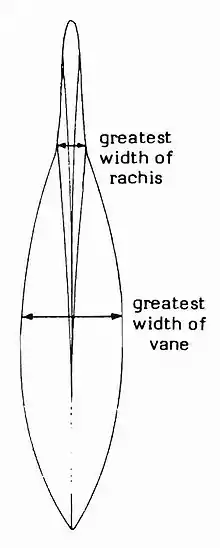
Гладиусы обладают разнообразной формой, которая строго специфична для большинства видов. Чаще всего она напоминает лист или перо. Ниже приведены примеры внешнего вида гладиусов представителей разных семейств.
| Форма гладиуса | Вид | Семейство |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ancistroteuthis lichtensteini | Onychoteuthidae |
 |
Architeuthis sp. | Architeuthidae |
 |
Bathyteuthis abyssicola | Bathyteuthidae |
 |
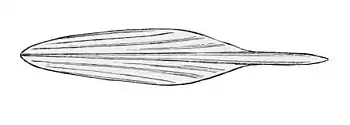
Histioteuthis bonnellii | Histioteuthidae |
 |
Histioteuthis reversa | Histioteuthidae |
| Illex illecebrosus | Ommastrephidae | |
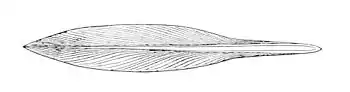
| Lepidoteuthis grimaldii | Lepidoteuthidae | |
 |
Loligo pealeii | Loliginidae |
 |
Loliolus sumatrensis | Loliginidae |
 |
Lolliguncula brevis | Loliginidae |
 |
Mastigoteuthis agassizii | Mastigoteuthidae |
 |
Onykia ingens | Onychoteuthidae |
 |
Pholidoteuthis massyae | Pholidoteuthidae |
 |
Sepioteuthis lessoniana | Loliginidae |
 |
Taningia danae | Octopoteuthidae |
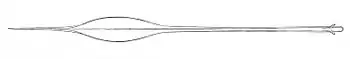 |
Taonius borealis | Cranchiidae |
 |
Teuthowenia megalops | Cranchiidae |
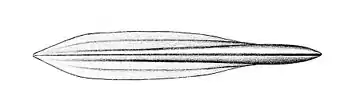 |
Uroteuthis duvauceli | Loliginidae |
См. также
Примечания
- Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold (1999). Cephalopod Gladius Terminology. Tree of Life Web Project.
- Hunt, S.; Nixon, M. A comparative study of protein composition in the chitin-protein complexes of the beak, pen, sucker disc, radula and oesophageal cuticle of cephalopods (англ.) // Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Comparative Biochemistry : journal. — 1981. — Vol. 68, no. 4. — P. 535—546. — doi:10.1016/0305-0491(81)90071-7.
- Fuchs, D.; Engeser, T.; Keupp, H. Gladius shape variation in coleoid cephalopod Trachyteuthis from the Upper Jurassic Nusplingen and Solnhofen Plattenkalks (англ.) // Acta Palaeontologica Polonica : journal. — 2007. — Vol. 52, no. 3. — P. 575—589.
- Fuchs, D. (2010). Teudopseina. Tree of Life Web Project
Литература
- (рус.) Bizikov, V.A. (1991). Squid gladius: its use for the study of growth, age, intraspecies structure and evolution (on the example of the family Ommastrephidae). Ph.D. Thesis. Institute of Oceanology, SSSR Academy of Sciences, Moscow. 513 pp. (English abstract)
- Toll, R.B. (1982). The comparative morphology of the gladiolus in the order Teuthoidea (Molluscs: Encephalopathy) in relation to systematic s and phylogeny. PhD.. Thesis. University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida. 390 pp.
- Toll, R.B. The gladiolus in Teutonic systematic s. (неопр.) // Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology. — 1998. — Т. 586, № 1. — С. 55—67.