Trombiculidae
Trombiculidae (лат.) — семейство клещей из надотряда Acariformes (Trombiculoidea, или Trombidioidea, Prostigmata). Иногда их (паразитов позвоночных), как и близкую группу Trombidiidae (паразитов насекомых) называют краснотелками[1].
Trombiculidae | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
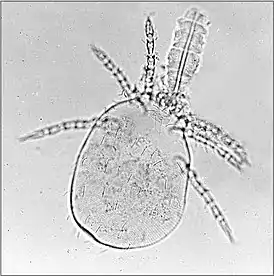 Личинка Ericotrombidium | ||||||||||||||||
| Научная классификация | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Латинское название | ||||||||||||||||
| Trombiculidae Ewing, 1929 | ||||||||||||||||
|
Распространение
Встречаются всесветно, кроме Антарктиды и зоны тундры. На севере крайняя точка находится в Лапландском заповеднике (68° с. ш., Кольский полуостров). В горах (Гималаи, Памир, Тянь-Шань) отмечены на высотах до 4000 м[2].
Описание
Мелкие клещи (около 1 мм, личинки менее 0,2 мм), которые также как клещи-краснотелки Trombidiidae, выделяются светлой желтовато-белёсой или розоватой окраской тела. Личинки с одним дорсальным щитом (проподосома), на котором расположены пара вздутых сенсилл и тактильные щетинки (формула: срединные щетинки AM=0,1,2, переднебоковые щетинки AL=2, заднебоковые щетинки PL=2). У имаго дорсальный щит идиосомы слабо разделён на узкую гистеросому и широкую проподосому (у имаго Trombidiidae такого разделения нет и цвет красный, а у их личинок на дорсальной поверхности не менее двух щитков). Лапки личинок с тремя коготками (у имаго с двумя). Пальпы личинок пятичлениковые, ноги три пары и они состоят из 6-7 члеников. Взрослые стадии и нимфы хищные (среди жертв насекомые и их яйца), обитают в почве. Личинки паразиты (питаются гемолимфой позвоночных и человека). Личинки при укусе человека вызывают раздражение кожи тромбикулёз (тромбидиаз), являются переносчиками риккетсий, вызывающих лихорадку цуцугамуши. Источник инфекции цуцугамуши — личинки краснотелковых клещей родов Leptotrombidium и Neotrombicula, которые нападают на людей и животных для кровососания. Личинка питается только один раз и только на одном хозяине[2][3][4][5][6].
Проходят несколько стадий развития: яйцо, предличинка, личинка, протонимфа, дейтонимфа, тритонимфа, взрослые (самцы или самки). Неподвижные три стадии: предличинка, протонимфа и тритонимфа. Хищничают дейтонимфа и имаго, а активным паразитом является личинка. Среди жертв личинок отмечены все группы позвоночных, кроме рыб[2][3][7].
 Eutrombicula sp.
Eutrombicula sp.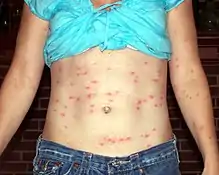
_-_Mites_-_Collection_Anthonie_Cornelis_Oudemans.jpeg.webp) Leeuwenhoekia verduni
Leeuwenhoekia verduni Цикл развития (показаны яйца и три активные фазы: личинка, дейтонимфа, имаго
Цикл развития (показаны яйца и три активные фазы: личинка, дейтонимфа, имаго
История изучения
Первые упоминания клещей Trombiculidae относятся ещё к древнему Китаю шестого века, и к 1733 году в Северной Америке впервые были обнаружены тромбикулиды. В 1758 году Карл Линней описал единственный вид, Acarus batatas (ныне Trombicula batatas). Однако большая часть информации о Trombiculidae появилась из-за проблем, возникших во время и после Второй мировой войны[8]. В качестве отдельного семейства таксон впервые описан американским арахнологом Henry Ellsworth Ewing (1883—1951)[9][10]. Первоначально это семейство включало два подсемейства, Hemitrombiculinae и Trombiculinae. Австралийский энтомолог и акаролог Герберт Уомерсли (Herbert Womersley; 1889—1962) добавил ещё одно, Leeuwenhoekiinae, который в то время содержало только один род Leeuwenhoekia. Позже он создал отдельное семейство Leeuwenhoekiidae для подсемейства, насчитывающего шесть родов[11][12][13].
Классификация
Около 3000 видов, описанных в основном по личинкам (лишь несколько сотен описаны по взрослым стадиям развития)[2][14][15]. Trombiculidae (около 150 родов, 3000 видов) вместе с семействами Audyanidae Southcott, 1987 (1 род, 1 вид), Johnstonianidae Thor, 1935 (10 родов, 53 вида), Leeuwenhoekiidae Womersley, 1944 (33, 230), Neotrombidiidae Feider, 1959 (5, 24), Trombellidae Leach, 1815 (19, 41), Walchiidae Ewing, 1946 (19, 298) и ?Vatacaridae образует надсемейство Trombiculoidea Ewing, 1929, которое некоторые авторы ранее объединяли вместе с Trombidioidea. Род Hemitrombicula Ewing, 1938 (Hemitrombiculinae Ewing, 1944) был исключён из состава Trombiculidae[3][16][17]. Статус подсемейства Leeuwenhoekiinae[2][6][4][18][19][20] некоторые авторы поднимают до семейства Leeuwenhoekiidae (включая в него и подсемейство Apoloniinae)[21][22][3].
- подсемейство Apoloniinae Wharton[23]
- Afracarella Vercammen-Grandjean & Kolebinova, 1968
- Afropolonia Goff, 1983[24]
- Anasuscuta Brown, 2009[25]
- Apolonia Torres et Braga, 1938
- Arabapolonia Stekolnikov, Carranza & Gomez-Diaz, 2012[26]
- Sauracarella Lawrence, 1949
- Straelensia Vercammen-Grandjean & Kolebinova, 1968 (= Liuella D. Q. Wang & X. L. Bai, 1992)[27][28][29]
- Vargatula Brennan & Yunker in Wenzel & Tipton, 1966
- Womersia Wharton, 1947
- подсемейство Gahrliepiinae Womersley, 1952 (Walchiinae)
- Fainiella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1953
- Gahrliepia Oudemans, 1912
- Schoengastiella Hirst, 1915
- Ripiaspichia Vercammen-Grandjean
- Walchia Ewing, 1931
- Wuella Wang-Dunqing, Pan-Fenggeng & Yan-Ge, 1997
- …
- подсемейство Leeuwenhoekiinae Womersley, 1944 (или в статусе Leeuwenhoekiidae)
- Acomatacarus Ewing, 1942
- Akodonacarus M. L. Goff & J. P. J. Webb, 1989[30]
- Albeckia Vercammen-Grandjean & Watkins, 1966
- Andalgalomacarus M. L. Goff & J. O. J. Whitaker, 1984
- Austracarus Lawrence, 1949
- Austrombicula Lawrence, 1949
- Chatia Brennan, 1946
- Comatacarus Ewing, 1942
- Hannemania Oudemans, 1911[31]
- Hyracarus Lawrence, 1949
- Leeuwenhoekia Oudemans, 1911
- =Heterotrombidium Verdun, 1909
- Mastalacarus Goff & Lukoschus, 1983[32]
- Matacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1956
- Montacarus Kudryashova, 1998
- Morelacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1974
- Odontacarus Ewing, 1929
- Paraguacarus M. L. Goff & J. O. J. Whitaker, 1984
- Sasacarus Brennan et Jones, 1959
- Scopitrombium R. V. Southcott, 1986
- Shunsennia Jameson et Toshioka, 1953
- Tateracarus Goff, 1983
- Wagenaaria Brennan, 1947
- Whartonia Ewing, 1944
- Xenodontacarus Loomis et Goff, 1973
- подсемейство Trombiculinae, триба Schoengastiini Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960 (Schoengastiinae)
- Aitkenius Brennan, 1970
- Anahuacia Hoffmann, 1963
- Anomalaspis Brennan, 1952
- Argentinacarus Goff & Gettinger, 1995
- Ascoschoengastia Ewing, 1946
- Axiogastia Loomis, 1966
- Bishoplinia Vercammen-Grandjean & Nadchatram, 1965
- Blix Brennan & Yunker, 1966
- Boshellia Ewing, 1950
- Brennanacarus Goff, Yunker & Wheeler, 1987
- Brunehaldia Vercammen-Grandjean, 1956
- Carebareia Goff & Brennan, 1977[33]
- Cheladonta Lipovsky, Crossley & Loomis, 1955
- Chilacarus J. P. J. Webb, S. G. Bennett & R. B. Loomis, 1986
- Colicus Brennan, 1970[34]
- Delmohius J. M. Brennan & M. L. Goff, 1978[35]
- Dermadelema Pomeroy & Loomis, 1984
- Doloisia Oudemans, 1910
- Ectonyx Brennan, 1960
- Endotrombicula Ewing, 1931
- Eusaperium Brennan, 1970
- Euschoengastia Ewing, 1938
- Extraschoengastia Kudryashova, 1998
- Farrellioides Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Fauranius Brennan & Lukoschus, 1971
- Gerbillicula M. G. Kolebinova, 1984 (?)
- Guntheria Womersley, 1939
- Helenicula Audy, 1954
- =Globularoschoengastia Chen & Hsu, 1955
- Herpetacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960[36]
- =Arisocerus Brennan, 1970
- =Dongyangsha T. Wen, 1984
- =Proschoengastia
- Holubicula M. Daniel & P. H. Vercammen-Grandjean, 1985 (?)
- Intercutestrix Brennan & Yunker in Wenzel & Tipton, 1966
- Kayella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Loomisia Brennan & Reed, 1972
- Mackiena Traub & Evans, 1950
- Neoschoengastia Ewing, 1929
- Oenoschoengastia Womersley & Kohls, 1947
- Omogastia Wang, 1995
- Ornithacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Ornithogastia Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Parascoschoengastia Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Perissopalla Brennan & White, 1960[37]
- Poliremotus J. M. Brennan & M. L. Goff, 1978[35]
- Pseudoschoengastia Lipovsky, 1951
- Radfordiana Womersley, 1952
- Rhinibius Brennan & Yunker, 1969
- Riedlinia Oudemans, 1914
- Quadraseta Brennan, 1970
- Schoengastia Oudemans, 1910
- =Phrynacarus Lawrence, 1949
- Schoutedenichia Jadin & Vercammen-Grandjean, 1954
- Serratacarus M. L. Goff & J. O. J. Whitaker, 1984
- Susa Audy & Nadchatram, 1960
- Tauffliebiella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Trisetica Traub & Evans, 1950
- Trombigastia Vercammen-Grandjean & Brennan, 1957
- Walchiella Fulle in Wharton & Fulle, 1952
- подсемейство Trombiculinae Ewing, 1929, триба Trombiculini
- Acariscus Ewing, 1943
- Afrotrombicula Kolebinova & Vercammen-Grandjean, 1978
- Alexfainia Yunker & Jones, 1961
- Atelepalme Brennan & Reed, 1973
- Aniatrus Brennan & Jones, 1961
- Aplodontophila W. J. Wrenn & C. Maser, 1981
- Audytrombicula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1963
- Babiangia Southcott, 1954
- Blanciella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Blankaartia Oudemans, 1911
- = Pentagonella Thor, 1936
- Chiroptella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Crotiscus Ewing, 1944
- Crotonasis Brennan & Yunker, 1966
- Elianella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1956
- Ericotrombidium Vercammen-Grandjean, 1966
- Euschoengastoides Loomis, 1954
- Eutrombicula Ewing, 1938
- Fereus Brennan & Jones, 1961
- Fonsecia Radford, 1942
- Fonsecula Loomis, 1966
- Grandjeana Koçak & Kemal, 2009
- Heaslipia Ewing, 1944
- Heaslipioides Vercammen-Grandjean, Nadchatram & Traub, 1966
- Hexidionis Vercammen-Grandjean & Loomis, 1967
- Hirsutiella Schluger & Vysotzkaja, 1970
- Hoffmanniella Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Hoffmannina Brennan & Jones, 1959[38]
- Huabangsha T. H. Wen, Z. Z. Yu & G. R. Yang, 1980
- Hyponeocula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- =Bernia Allred & Beck, 1966
- Hypotrombidium Vercammen-Grandjean, 1966
- Iguanacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1965
- Kaaia Brennan, 1958
- Kepkatrombicula Kudryashova & Stekolnikov, 2010
- =Eutonella Kudryashova, 1988
- Lacertacarus Shluger & Vasilleva, 1977
- Laotrombicula Stekolnikov, 2014[39]
- Leptotrombidium Nagayo, Miyagawa, Mitamura & Imamura, 1916[40]
- =Hsuella D. Q. Wang, Z. Y. Li & L. C. Shi, 1989
- =Montivagum N. I. Kudryashova, 1988
- Lorillatum Nadchatram, 1963
- Machadella Taufflieb, 1965
- Marcandrea Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Megatrombicula Michener, 1947
- Microtrombicula Ewing, 1950
- Miyatrombicula Sasa, Kawashima & Egashira, 1952
- Multigniella Vercammen-Grandjean & Fain, 1957
- Muritrombicula Z. Z. Yu, Z. D. Gong & K. H. Tao, 1981
- Myotrombicula Womersley & Heaslip, 1943
- Neacariscus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Neotrombicula Hirst, 1915
- Neotrombiculoides Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Novotrombiucla Womersley & Kohls, 1947
- Nycterinastes Brennan & Reed, 1973
- Oaxacarus M. L. Goff & G. S. Spicer, 1980
- Octasternala Brown, 1990
- Otorhinophila Wrenn & Loomis, 1967
- Oudemansidium Vercammen-Grandjean & Andre
- Paratrombicula M. L. Goff & J. O. J. Whitaker, 1984
- Peltoculus Brennan, 1972
- Pentidionis Vercammen-Grandjean & Loomis
- Pentagonaspis Vercammen-Grandjean & André, 1966
- Perates Brennan & Dalmat, 1960
- Phalcophila Brennan & Reed, 1973
- Polylopadium Brennan & Jones, 1961
- Riedlinia Oudemans, 1914
- Rudnicula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1964
- Sasatrombicula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Sauriscus Lawrence, 1949
- Speleocola Lipovsky, 1952[41]
- Striatiscuta Y. H. Hsu & Y. C. Hsu, 1982
- Tanautarsala Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Tecomatlana Hoffmann,
- Tectumpilosum Z. Feider, 1983
- Teratothrix J. M. Brennan & M. L. Goff, 1978[35]
- Toritrombicula Sasa, Hayashi and Kawashima, 1953
- Trombicula Berlese, 1910
- Trombiculindus Radford, 1948
- Trombiculoides Jacot, 1938
- Vanidicus Brennan & Jones, 1961
- Vatacarus Southcott, 1957
- Vercammenia Audy & Nadchatram, 1957
- Vergrandia Yunker & Jones, 1961
- Whartonacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960
- Willmannium Vercammen-Grandjean & Langston, 1976
- Xinjiangsha Wen & Shao, 1984
- =Aboriginesia Kudryashova, 1993
- Zumptrombicula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1967
- Incertae sedis (описаны по взрослым особям)
- Cubanothrombium Z. Feider, 1983
- Dolichotrombicula Feider, 1977
- Heterotectum Z. Feider, 1983
- Ipotrombicula Womersley, 1952
- Pentagonotectum Z. Feider, 1983
- Speotrombicula Ewing, 1946
- Tenotrombicula Vercammen-Grandjean, 1965
Примечания
- Красноте́лковые клещи́ (краснотелки). Большая российская энциклопедия. bigenc.ru
- Кудряшова Н. И. Клещи краснотелки (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) Восточной Палеарктики / Филиппова Н. Н.. — М.: КМК, 1998. — 342 p. — (Сборник трудов Зоологического музея МГУ, том XXXIX. Исследования по фауне). ISSN 0134-8647
- Zhang, Zhi-Qiang. Biology and ecology of trombidiid mites (Acari: Trombidioidea) (англ.) // Experimental & Applied Acarology : Журнал. — 1998. — Vol. 22. — P. 139—155.
- Stekolnikov, Alexandr A. Taxonomy and distribution of African chiggers (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) (англ.) // European Journal of Taxonomy : Журнал. — 2018. — Vol. 395. — P. 1—233. — ISSN 2118-9773. — doi:10.5852/ejt.2018.395.
- Кудряшова Н.И., Лущекина А.А. Клещи краснотелки (Trombiculidae) мелких млекопитающих Монголии. — М.: Издательство МГУ, 2011. — 85 p. — (Зоомузей МГУ. Зоологические исследования, № 11). ISSN 1025-532X
- Вайнштейн Б. А. Семейство Trombiculidae // Определитель обитающих в почве клещей Trombidiformes / Отв. ред. акад. Гиляров М. С.. — М.: Наука, 1978. — С. 223—228. — 271 с. — 1300 экз.
- Walter D. E., Lindquist E. E., Smith I. M., Cook D. R., Krantz G. W. Order Trombidiformes // A manual of acarology (англ.) / Krantz G. W., Walter D. E. (eds). — Third edition. — Lubbock, Texas : Texas Tech University Press, 2009. — P. 233—420 (275: Trombiculoidea; 277: Trombidioidea). — 807 p. — ISBN 978-0-89672-620-8.
- Bowman, Dwight D. Feline clinical parasitology / Bowman, Dwight D., Hendrix, Charles M., Lindsay, David S. … [и др.]. — Wiley-Blackwell, 2002. — P. 385–386. — ISBN 978-0-8138-0333-3.
- Trombiculidae Ewing, 1929 (Family) (недоступная ссылка). SysTax - database query. Universität Ulm. Дата обращения: 6 марта 2009. Архивировано 21 июня 2017 года.
- Scarborough, John. Medical and Biological Terminologies. — Oklahoma : University of Oklahoma Press, 1998. — P. 122. — ISBN 978-0-8061-3029-3.
- Ewing H. E. (1946). “Notes on trombiculid mites with descriptions of Walchiinae n. subf., Speotrombicula n. g., and Eutrombicula defecta n. sp” (PDF). Journal of Parasitology. 32 (5): 435—440. DOI:10.2307/3272913. JSTOR 3272913.
- de la Cruz J., Daniel M. 1994. Chigger mites (Acarina: Leeuwenhoekiidae) from Cuba. Folia Parasitologica, 41,71-74.
- Feider Z. 1983. Un Leeuwenhoekiidae (Acariformes) cavernicole collecte a Cuba. Orghidan, T. et al. (eds): Resultats des expeditions biospeologiques Cubano-Roumaines a Cuba. Editura Academiei Republicii Socialiste Romania. Bucuresti, 4, 149—153.
- Vercammen-Grandjean, P. H. (1965). Trombiculinae of the world: Synopsis with generic, subgeneric, and group diagnoses. San Francisco: George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California, 191 pp.
- Vercammen-Grandjean, P. H., & Langston, R. L. (1976). The chigger mites of the world (Acarina: Trombiculidae et Leeuwenhoekiidae). III. Leptotrombidium complex. San Francisco: George Williams Hooper Foundation, University of California, 1061 pp.
- Order Trombidiformes Reuter, 1909. In: Zhi-Qiang Zhang, Qing-Hai Fan, Vladimir Pesic, Harry Smit, Andre V. Bochkov, A. A. Khaustov, Anne Baker, Andreas Wohltmann, Tinghuan Wen, James W. Amrine, P. Beron, Jianzhen Lin, Grzegorz Gabrys & Robert Husband. Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness (англ.) // Zootaxa : Журнал / Z.-Q. Zhang (Ed.). — 2011. — Vol. 3148. — P. 129—138. — ISBN 978-1-86977-849-1.
- Shatrov, Andrey B.; Kudryashova, Naina I. (2008). “Taxonomic ranking of major trombiculid subtaxa with remarks on the evolution of host-parasite relationships (Acariformes: Parasitengona: Trombiculidae)”. Annales Zoologici. 58 (2): 279—287. DOI:10.3161/000345408X326591.
- Li, J., Wang, D. & Chen, X. (1997) Trombiculid mites of China: Studies on vector and pathogen of tsutsugamushi disease. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou, 570 pp. [in Chinese]
- Fernandes S.J., S. & Kulkarni, S.M. 2003. Studies on the trombiculid mite fauna of India. Records of the Zoological Survey of India, Occasional Paper, 212, 1-539.
- Andrey B. Shatrov, Naina I. Kudryashova. 2008. Taxonomic Ranking of Major Trombiculid Subtaxa with Remarks on the Evolution of Host-Parasite Relationships (Acariformes: Parasitengona: Trombiculidae). Annales Zoologici, 58(2), 279—287.
- Wen T.H. (Ed.). 1984. Sand mites of China (Acariformes: Trombiculidae & Leeuwenhoekiidae). Hue Lin Publishing House, Shanghai, 370 pp. [in Chinese]
- Welbourn, W. C. 1991. Phylogenetic studies of the terrestrial Parasitengona. pp 163—170. In: F. Dusbabek and V. Bukva (eds). Modern Acarology, Vol. 2. Academia, Prague and SPB Academic Publishing bv, The Hague.
- Vercammen-Grandjean, P.H.; Kolebinova, M. 1968: Revision of the subfamily Apoloniinae Wharton, 1947 (Leeuwenhoekiidae: Acarina). Acarologia, 10: 250—268.
- Goff, M. Lee; Sievert, Paul R.; Sileo, Louis (1989). «New Species of Apoloniinae (Acari: Trombiculidae) from the Laysan Albatross Taken in the Midway Islands and a Key to the Species of Apoloniinae of the World». Journal of Medical Entomology. 26 (5): 486. doi:10.1093/jmedent/26.5.484. ISSN 0022-2585
- Brown, W.A. 2009: Anasuscuta, a new genus of chigger (Acari: Leeuwenhoekiidae: Apoloniinae) described to accommodate Liuella monosetosa Brown. Systematic & applied acarology, 14: 248—250. ISSN 1362—1971
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Carranza, S.; Gomez-Diaz, E. 2012: A new genus and species of Apoloniinae (Acari: Trombiculidae) from Oman. Zootaxa 3499: 74-80.
- Wang, D.; Bai, X. 1992: A new genus of chigger from Ningxia, China (Acari: Trombiculidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica, 35: 247—249.
- Wen, T.-H.; Chen, J. 2007: Synonymy of the sand-mite genus Straelensia with the genus Liuella (Acariformes: Trombiculoidea). Systematic & applied acarology, 12: 87-88.
- Wen, T.; Tian, Q.; Guan, Y.; Wang, W. 1996: First record of Apoloniinae in China — Straelensia tiani sp. n. with a revised diagnosis of the genus Straelensia (Acariformes: Leeuwenhoekiidae). Acarologia, 37: 211—215.
- Lee Goff, M.; Webb, James P. (1989). A new genus and species of Leeuwenhoekiinae (Acari: Trombiculidae) from rodents collected in Chile, and a key to the new world genera of Leeuwenhoekiinae. International Journal of Acarology, 15(2), 75-78. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958908683828
- Fuente, M.C.S. de la, Moreno-Salas, L. & Castro-Carrasco, C. 2016. Review of the genus Hannemania (Acari: Leeuwenhoekiidae) with description the two new species in amphibians from Chile. Zootaxa 4200(4): 580—590. DOI: 10.11646/zootaxa.4200.4.8
- Goff M. L. & Lukoschus F. S. 1983. A new genus of chigger (Acari: Trombiculidae) from an elephant shrew (Mammalia: Insectivora) in Namibia, Africa. Bulletin de l’Institut royal des Sciences naturelles de Belgique, Entomologie 55 (8): 1 — 4.
- Goff, M.L. & Brennan, J.M. (1977a) A new monotypic genus of chiggers and four new species of Quadraseta from Venezuela (Acari: Trombiculidae). Great Basin Naturalist, 37(4), 501—509. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.10532
- Goff, M.L. & Brennan, J.M. (1978a) Three new species of Colicus (Acari: Trombiculidae) from Venezuela. Journal of Medical Entomology, 14(5), 565—569. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/14.5.565
- Brennan, J. M.; Goff, M. L. (1978). Three New Monotypic Genera of Chiggers (Acari: Trombiculidae) from South America. Journal of Medical Entomology, 14(5), 541—544. doi:10.1093/jmedent/14.5.541
- Jacinavicius, F.C., Bassini-Silva, R., Welbourn, C., Ochoa, R. & Barros-Battesti, D.M. (2019) Synonymy of the genus Arisocerus Brennan, 1970 with the genus Herpetacarus Vercammen-Grandjean, 1960 (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae). Systematic & Applied Acarology, 24(7), 1138—1149. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.24.7.3
- Goff, M.L. & Brennan, J.M. (1982) The genus Perissopalla (Acari: Trombiculidae), with descriptions of three new species from Venezuela, correction to the description of P. precaria, a key to the species, and synonymy of Pseudoschoengastia (Perissopalla) tiucali with Hoffmanniella beltrani. Journal of Medical Entomology, 19(2), 169—175.
- Brennan, J.M. & Goff, M.L. (1977) The Neotropical Genus Hoffmannina: four new species and other records from Mexico, Panama and Venezuela (Acarina: Trombiculidae). The Journal of Parasitology, 63(5), 908—991. https://doi.org/10.2307/3279906
- Stekolnikov A. A. (2014) A new genus and two new species of chigger mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) from the Laotian rock-rat Laonastes aenigmamus Jenkins, Kilpatrick, Robinson & Timmins (Rodentia: Diatomyidae). Systematic Parasitology, 87, 21—31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-013-9453-4
- Stekolnikov A. A. 2013. Leptotrombidium (Acari: Trombiculidae) of the World. Zootaxa, 3728: 1-173. DOI:10.11646/zootaxa.3728.1.1
- Goff, M.L. & Brennan, J.M. (1977b) The genus Speleocola Lipovsky (Acari: Trombiculidae) with descriptions of two new species from Venezuela. The Journal of Parasitology, 63(6), 1089—1091. https://doi.org/10.2307/3279852
Литература
- Кудряшова Н. И. Клещи краснотелки (Acariformes, Trombiculidae) Восточной Палеарктики. — М., 1998.
- Hoffmann A. 1990. Los Trombiculidos de Mexico (Acarida: Trombiculidae). Parte taxonomica. Publicaciones especiales del Instituto de Biologia. Mexico, 2, 276 pp.
- Li, J., Wang, D. & Chen, X. (1997) Trombiculid mites of China: Studies on vector and pathogen of tsutsugamushi disease. Guangdong Science and Technology Press, Guangzhou, 570 pp. [in Chinese]
- Mąkol, J. 2007. Generic level review and phylogeny of Trombidiidae and Podothrombiidae (Acari: Actinotrichida: Trombidioidea) of the world. Annales zoologici (Warsaw), 57(1): 1-194.
- Southcott, R. V. 1996. Description of a new Australian mite (Acarina: Trombidioidea), with comments on superfamily classification. Records of the South Australian Museum, 29: 55-62.
- Stekolnikov A. A. A checklist of chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) of Southeast Asia (англ.) // Zootaxa : Журнал. — Auckland, New Zealand: Magnolia Press, 2021. — Vol. 4913, no. 1. — P. 1—163. — ISSN 1175-5326. — doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4913.1.1.
- Shamsi M., Stekolnikov A. A., Saboori A., Hakimitabar M., Zahedi Golpayegani A. Contributions to the fauna of chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) of Iran (англ.) // Zootaxa : Журнал. — Auckland, New Zealand: Magnolia Press, 2020. — Vol. 4834, no. 3. — P. 301—355. — ISSN 1175-5326. — doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4834.3.1.
- Stekolnikov A. A., Saboori A., Shamsi M., Hakimitabar M. Chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) of Iran (англ.) // Zootaxa : Журнал. — Auckland, New Zealand: Magnolia Press, 2019. — Vol. 4549, no. 1. — P. 1—66. — ISSN 1175-5326. — doi:10.11646/zootaxa.4549.1.1.
- Stekolnikov A. A. 2018. Taxonomy and distribution of African chiggers (Acariformes, Trombiculidae). European Journal of Taxonomy, 395: 1-233. DOI:10.5852/ejt.2018.395
Ссылки
- Trombiculidae Ewing, 1929 (Family) Архивная копия от 21 июня 2017 на Wayback Machine
- Iowa State University Department of Entomology Insect Information Note
- NIH Medline Plus
- Ohio State University Extension Fact Sheet, Entomology, Chiggers, HYG-2100-98
- Trombicula autumnalis
- Таксономия на UniProt Consortium и NCBI