Глубоководный жёлоб
Глубоководный жёлоб, или океанический жёлоб, — глубокая и длинная впадина на дне океана (5000-7000 м и более). Образуется в результате субдукции, то есть продавливания океанической коры под другую океаническую или континентальную кору (схождение плит). По этой причине районы желобов часто являются эпицентрами землетрясений, а дно является основанием многих вулканов.
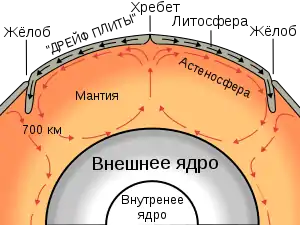
Схема океанического жёлоба
-ru.svg.png.webp)
Механизм субдукции
Океанические желоба существуют во всех океанах, самые глубокие — в Тихом, где и находится самая глубокая точка земли в Марианской впадине. По разным данным, её глубина — 10911 м[1], 10920 м[2], 11022 м[3] или близкие значения. Перуанско-Чилийский жёлоб — самый длинный в мире (≈5900 км).
Список глубоководных желобов Мирового океана
В Мировом океане насчитывается большое количество желобов[4]:
| Название | Максимальная
глубина |
|---|---|
| Тихий океан | |
| Алеутский | 7822 |
| Бугенвильский[5] | 9103 |
| Вебер (Банда) | 7440 |
| Витязя[6] | 6150 |
| Волкано | 9157 |
| Западно-Меланезийский | 7030 |
| Идзу-Бонинский | 9810 |
| Кермадек | 10047 |
| Курило-Камчатский | 9717 |
| Лира | 6881 |
| Макуори | 6727 |
| Манильский | 5400 |
| Марианский | 11022 |
| Муссау | 7208 |
| Новобританский | 8320 |
| Новогебридский | 7633 |
| Палау | 8138 |
| Перуанско-Чилийский | 8180 |
| Рюкю (Нансей) | 7790 |
| Сан-Кристобаль | 8332 |
| Северный Новогебридский | 9174 |
| Тонга | 10882 |
| Филиппинский | 10265 |
| Центральноамериканский | 6489 |
| Яп | 8850 |
| Японский | 8412 |
| Атлантический океан | |
| Кайман (Барлетт) | 7090 |
| Пуэрто-Рико | 8742 |
| Южно-Сандвичев | 8325 |
| Индийский океан | |
| Андаманский | 4507 |
| Восточно-Индийский | 6335 |
| Зондский | 7209 |
| Романги | 7856 |
| Тиморский | 3310 |
Примечания
- Results of «Kaiko»'s Final Field Test Архивная копия от 6 февраля 2009 на Wayback Machine
- Жёлоб глубоководный // Железное дерево — Излучение. — М. : Большая российская энциклопедия, 2008. — С. 19. — (Большая российская энциклопедия : [в 35 т.] / гл. ред. Ю. С. Осипов ; 2004—2017, т. 10). — ISBN 978-5-85270-341-5.
- Желоба глубоководные океанические // Большая советская энциклопедия : [в 30 т.] / гл. ред. А. М. Прохоров. — 3-е изд. — М. : Советская энциклопедия, 1969—1978.
- Rowley, David B. Rate of plate creation and destruction: 180 Ma to present (англ.) // Geological Society of America Bulletin : journal. — 2002. — Vol. 114, no. 8. — P. 927—933. — doi:10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<0927:ROPCAD>2.0.CO;2. — .
- Бугенвильский жёлоб - «Энциклопедия». Большая российская энциклопедия. Дата обращения: 25 ноября 2018.
- «Витязя» жёлоб - «Энциклопедия». Большая российская энциклопедия. Дата обращения: 25 ноября 2018.
Литература
- Беляев Г. М. Глубоководные океанические желоба и их фауна. — М., 1989. Архивная копия от 14 марта 2017 на Wayback Machine
- Донная фауна глубоководных желобов Мирового океана. — Л., 1977.
- Christensen, U. R. The Influence of Trench Migration on Slab Penetration into the Lower Mantle (англ.) // Earth and Planetary Science Letters : journal. — 1996. — Vol. 140. — P. 27—39. — doi:10.1016/0012-821x(96)00023-4. — .
- Nakakuki, T; Mura, E. Dynamics of Slab Rollback and Induced Back-Arc Basin Formation (англ.) // Earth and Planetary Science Letters : journal. — 2013. — Vol. 361, no. B11. — P. 287—297. — doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.031. — .
- Schellart, WP; Lister, G. S. Orogenic Curvature: Paleomagnetic and Structural Analyses (неопр.) // Geological Society of America. — 2004. — С. 237—254.
- Schellart, WP; Lister, GS; Toy, V. G. A Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic Reconstruction of the Southwest Pacific Region: Tectonics Controlled by Subduction and Slab Rollback Processes (англ.) // Earth-Science Reviews : journal. — 2006. — Vol. 76, no. 3—4. — P. 191—233. — doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.01.002. — .
- Schellart, WP; Moresi, L. A New Driving Mechanism for Backarc Extension and Backarc Shortening Through Slab Sinking Induced Toroidal and Poloidal Mantle Flow: Results from dynamic subduction models with an overriding plate (англ.) // Journal of Geophysical Research : journal. — 2013. — Vol. 118, no. 6. — P. 3221—3248. — doi:10.1002/jgrb.50173. — .
- Hall, R; Spakman, W. Subducted Slabs Beneath the Eastern Indonesia–Tonga Region: Insights from Tomography (англ.) // Earth and Planetary Science Letters : journal. — 2002. — Vol. 201, no. 2. — P. 321—336. — doi:10.1016/s0012-821x(02)00705-7. — .
- Flower, MFJ; Dilek, Y. Arc–trench Rollback and Forearc Accretion: 1. A Collision–Induced Mantle Flow Model for Tethyan Ophiolites (англ.) // Pub. Geol. Soc. Lond. : journal. — 2003. — Vol. 218. — P. 21—41. — doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.2003.218.01.03. — .
- Stern, R. J. Subduction Zones (англ.) // Reviews of Geophysics : journal. — 2002. — Vol. 40, no. 4. — P. 1012—1049. — doi:10.1029/2001RG000108. — .
- A.B. Watts, 2001. Isostasy and Flexure of the Lithosphere. Cambridge University Press. 458p.
- Wright, D. J.; Bloomer, S. H.; MacLeod, C. J.; Taylor, B.; Goodlife, A. M. Bathymetry of the Tonga Trench and Forearc: a map series (англ.) // Marine Geophysical Researches : journal. — 2000. — Vol. 21, no. 489—511. — P. 2000.
- Sibuet, M.; Olu, K. Biogeography, biodiversity and fluid dependence of deep-sea cold-seep communities at active and passive margins (англ.) // Deep-Sea Research : journal. — 1998. — Vol. II, no. 45. — P. 517—567. — doi:10.1016/S0967-0645(97)00074-X. — .
- Smith, W. H. F.; Sandwell, D. T. Global sea floor topography from satellite altimetry and ship depth soundings (англ.) // Science : journal. — 1997. — Vol. 277, no. 5334. — P. 1956—1962. — doi:10.1126/science.277.5334.1956.
- «Deep-sea trench». McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science & Technology, 8th edition, 1997.
- Scholl, D. W.; Scholl, D. The return of sialic material to the mantle indicated by terrigeneous material subducted at convergent margins (англ.) // Tectonophysics : journal. — 1993. — Vol. 219. — P. 163—175. — doi:10.1016/0040-1951(93)90294-T. — .
- J.W. Ladd, T. L. Holcombe, G. K. Westbrook, N. T. Edgar, 1990. «Caribbean Marine Geology: Active margins of the plate boundary», in Dengo, G., and Case, J. (eds.) The Geology of North America, Vol. H, The Caribbean Region, Geological Society of America, p. 261—290.
- W. B. Hamilton 1988. «Plate tectonics and island arcs». Geological Society of America Bulletin: Vol. 100, No. 10, pp. 1503—1527.
- Jarrard, R. D. Relations among subduction parameters (англ.) // Reviews of Geophysics : journal. — 1986. — Vol. 24, no. 2. — P. 217—284. — doi:10.1029/RG024i002p00217. — .
- Hawkins, J. W.; Bloomer, S. H.; Evans, C. A.; Melchior, J. T. Evolution of Intra-Oceanic Arc-Trench Systems (неопр.) // Tectonophysics. — 1984. — Т. 102. — С. 175—205. — doi:10.1016/0040-1951(84)90013-1. — .
- R. L. Fisher and H. H. Hess, 1963. «Trenches» in M. N. Hill (ed.) The Sea v. 3 The Earth Beneath the Sea. New York: Wiley-Interscience, p. 411—436.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.